Publications according to year
- Publication of a paper by Jan Veselý's group in The Journal of Organic Chemistry:
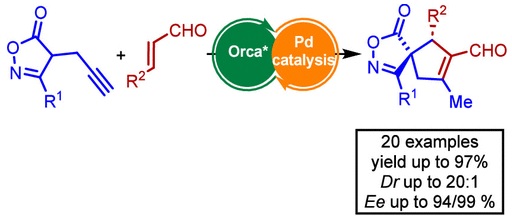
Enantioselective Synthesis of Spirocyclic Isoxazolones Using a Conia-Ene Type Reaction
Abstract: Stereoselective synthesis of spirocyclic compounds containing heterocyclic motifs represents a formidable challenge in enantioselective synthesis. Here, we present a cascade reaction between α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and isoxazolones under synergistic catalysis of a chiral secondary amine and a palladium(0) catalyst. This strategy allows access to chiral spiroisoxazolone derivatives with a large substrate scope tolerance and high levels of diastereoselectivity (dr up to 20:1) and enantioselectivity (up to 99% ee). Furthermore, the utility of this methodology is showcased by the transformation of chiral spiroisoxazolones into structurally attractive and enantiomerically enriched cyclopentene carboxylic acids with two stereogenic centers.
- Publication of a paper by Martin Kotora's group in the magazines Chemistry Views and Chemistry Europe:
Making the Photochemistry of Quinones More Predictable and User-Friendly (Chemistry Views)
Anticipating Natural Phenolics Through Visible Light-Induced Photorearrangement of Quinones (Chemistry Europe)
Abstract: A general protocol for the photorearrangement of substituted benzo- and naphthoquinones using monochromatic blue light irradiation in solution was developed. During this process, the quinone ring is transformed into the hydroquinone, while the substituent undergoes desaturation or annulation onto the proximal oxygen of the formed hydroquinone. We found that desaturation was preferred for acyclic saturated substituents, such as alkyl groups, and the tendency for annulation was observed for both cyclic and acyclic unsaturated substituents (allyl, alkenyl, aryl). The diversity of the participating substituents and the functional group tolerance of this transformation allowed us to prepare 10 natural phenolic compounds, suggesting that visible light may likewise induce their formation from the respective quinones in natural sources.

- Publication of a paper by Radim Hrdina's group in Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry:
C–H amination of enolizable and nonenolizable ketones
Abstract: We present a method for the amination of enolizable and non-enolizable ketones in the alpha (or beta) position to the carbonyl group. This approach is based on the conversion of the corresponding cyanohydrins to carbonazidates, precursors for thermal intramolecular nitrene insertion reactions into the adjacent C–H bond. Hydrolysis of the resulting carbamates under basic conditions with simultaneous regeneration of the carbonyl group yields amino ketones.

- Publication of a paper by Martin Kotora's group in Chemical Communications:
Synthesis of highly fluorescent helical quinolizinium salts by a Rh-catalyzed cyclotrimerization/C–H activation sequence
Abstract: A series of helical quinolizinium salts were prepared utilizing Rh-catalyzed [2+2+2]cyclotrimerization and C–H activation processes as the crucial synthetic steps. The cyclotrimerization of appropriately substituted diynes with trimethylsilylethyne under Rh-catalyzed conditions provided the 1-arylisoquinolines in up to 61% isolated yields. Their Rh-catalyzed C–H activation/annulation with various aryl and alkyl disubstituted alkynes gave rise to [7]-helical quinolizinium salts in high isolated yields (up to 93%). Enantioselective C–H activation was also tried with asymmetric induction up to 62% ee. The respective boron and platinum complexes of 1-arylisoquinolines were prepared as well. All prepared compounds exhibit fluorescence in the orange-red light region (606–682 nm) with ΦFs 28–99%.

- Publication of a paper by Jan Veselý's group in Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis:
Stereoselective N-Heterocyclic-Carbene-Catalyzed Spiroannulation as an Access Towards Spirobenzofuranone-Fused Cyclohexenones
Abstract: In this work, we present an organocatalytic spiroannulation method that provides access to spirocyclic benzofuran-2-ones. The reaction proceeds via the generation of an azolium dienolate from an α-bromo-α,β-unsaturated aldehyde using a chiral N-heterocyclic carbene, followed by annulation with benzofuran-2-one-derived alkenes. The resulting chiral spirobenzofuranone-fused cyclohexenones were obtained in 77–99% ee and dr from 1.2:1 to 20:1. The utility of the protocol was underscored by gram-scale reaction and follow-up transformations.
- Publication of a paper by Jan Veselý's group in Journal of Organic Chemistry:
Enantioselective Preparation of Cyclopentene-Based Amino Acid with a Quarternary Carbon Center
Abstract: Azlactone is an important starting material for synthesizing amino acids containing a quaternary α-carbon. In this study, we have developed a sequential “one-pot” procedure involving an enantioselective spirocyclization reaction followed by acidic azlactone opening, which led to amino acid derivatives. The key step of this procedure is a spirocyclization between propargylated azlactones and enals by using a cooperative catalytic approach that combines chiral secondary amine and achiral Pd(0) complexes. The final acid opening of the azlactone motif allows isolation of the corresponding amino acid derivatives as major diastereoisomers in yields ranging from 37% to 70% with enantioselectivities of 85–97% ee. These synthesized amino acid derivatives hold great potential in the pharmaceutical and bioactive compound industries. Moreover, the final amino acid products with a cyclopentene moiety can be further derivatized, opening up even more possibilities for their application.

- Publication of a paper by Lukáš Rýček's group in Chem Plus Chem:
Silver Complex Bearing N-Heterocyclic Carbene Bidentate Chelating Ligand as an Efficient Catalyst in Solvent-Free KA2 Coupling
Abstract: We report a synthesis of silver complexes bearing chelating bidentate N-heterocyclic carbene, with various substitutions at the terminal positions of the imidazole moiety of the NHC units. The long aliphatic substituents proved to be beneficial in terms of the synthetic efficiency of the complexes, compared to previously reported methyl substitution. The complexes demonstrated excellent suitability for the KA2 coupling reaction, providing quaternary carbon-containing propargylic amines in yields up to 95 %, under solvent-free conditions. The method showed high tolerance for a wide range of substrates, including naturally occurring ketones, underscoring its practicality. To our knowledge, this represents the first use of a well-defined silver species in KA2 coupling, marking an advancement in the field.
- Publication of a paper by Lukáš Rýček's group in ACS Bio & Med Chem Au:
Selagibenzophenone B and Its Derivatives: SelB-1, a Dual Topoisomerase I/II Inhibitor Identified through In Vitro and In Silico Analyses
Abstract: The development of multitargeted drugs represents an innovative approach to cancer treatment, aiming to enhance drug effectiveness while minimizing side effects. Herein, we sought to elucidate the inhibitory effect of selagibenzophenone B derivatives on the survival of cancer cells and dual topoisomerase I/II enzyme activity. Results demonstrated that among the compounds, SelB-1 selectively inhibited the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells while exhibiting minimal effects on healthy cells. Furthermore, SelB-1 showed a dual inhibitory effect on topoisomerases. Computational analyses mirrored the results from enzyme inhibition assays, demonstrating the compound’s strong binding affinity to the catalytic sites of the topoisomerases. To our surprise, SelB-1 did not induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells; instead, it induced autophagic gene expression and lipid peroxidation while reducing GSH levels, which might be associated with ferroptotic death mechanisms. To summarize, the findings suggest that SelB-1 possesses the potential to serve as a dual topoisomerase inhibitor and can be further developed as a promising candidate for prostate cancer treatment.
- Publication of a paper by Lukáš Rýček's group in Chem Plus Chem:
The Biomimetic Synthesis of Polyarylated Fluorenes, Relevant to Selaginellaceae Polyphenols, Leading to the Spontaneous Formation of Stable Radicals
Abstract: This work reports a biomimetic synthesis of polyarylated fluorene derivatives. The molecules are formed via intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution, resembling a cyclization leading towards the natural selaginpulvilins from selaginellins. The scope of the reaction was investigated, and the products were obtained in 60–95 % yields. Some of the compounds decompose to a stable radical. We investigated the nature and the origin of the radical using experimental methods, including EPR or electrochemical measurements, as well as theoretical methods, such as DFT calculations. Based on our observations, we hypothesize, that phenoxy radicals are formed in the first instance, which however undergo internal rearrangement to thermodynamically more stable carbon-centered radicals. The preliminary data also show the cytotoxic properties of some of the molecules.

- Publication of an article by Lukáš Rýček's group in the New Journal of Chemistry:
Internal 2D networking of silver bromide with a bidentate N-heterocyclic carbene ligand enables the formation of an inherently heterogeneous reusable catalyst for multicomponent A3 coupling
Abstract: We report the synthesis of a heterogenous silver catalyst stabilized by bidentate N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. The heterogeneous nature of the catalyst is inherently derived from the unprecedented internal structural features observed for the catalyst. X-ray studies show that the silver complex forms a two-dimensional cross-linked system, where one dimension of the network is formed by inorganic polymer strings and the second direction is formed by the interconnection of these inorganic strings with NHC bidentate ligands. This organized internal arrangement renders the complex insoluble in many common organic solvents and enables its utilization as a reusable heterogeneous catalyst in multicomponent A3 coupling reactions. Notably, propargylic amines were obtained with yields of up to 97%, and the catalyst demonstrated reusability for six cycles. These results can facilitate the further development of heterogeneous NHC catalysts.

Sulfinamide Crossover Reaction

- Book publication by Martin Kotora published by Springer:
Metallocenes in Regio- and Stereoselective Synthesis

- Publication of a paper by Michal Hocek's group in Nature Communications:

- Publication of a paper by Martin Kotora's group in Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry:
Biphenylene and 1-Azabiphenylene as a Platform for Synthesis of Azapolyaromatic Compounds
Abstract: Attempts to carry out intramolecular annulation of 9,10-diarylbenzo[h]quinolines and 9,10-di(hetero)arylphenanthrenes to aromatics with expanded π-conjugated systems by using different methods are described. The starting compounds (9,10-diarylbenzo[h]quinolines and 9,10-di(hetero)arylphenanthrenes) were prepared by C−C bond activation in 1-azabiphenylene or biphenylene followed by insertion of internal alkynes. Interestingly, unlike in purely carbon-based aromatics, the course of the annulation turned out to be highly dependent on the structure of maternal compounds. In a handful of cases were obtained the expected or desired products. In others, unexpected rearrangements of the basic molecular frameworks were observed.

- Publication of a paper by Jan Veselý's group in Nature Communications:
Organocatalytic desymmetrization provides access to planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophanes
- Publication of an article in collaboration between two groups of Radim Hrdina and Jindřich Jindřich in the Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry:
Spatial arrangements of cyclodextrin host–guest complexes in solution studied by 13C NMR and molecular modelling

- Publication of a paper by Eliška Matoušová's group in European Journal of Organic Chemistry:
Oxidative Cleavage and Ring Reconstruction for the Synthesis of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloid Analogues

- Publication of a paper by Ondřej Baszczyňski's group in Green Chemistry:
Multimetallic Pd- and Ni-catalyzed C(sp2)–P cross-coupling under aqueous micellar conditions

- Publication of a paper by Radim Hrdina's group v Molecules:

- Publication of a paper by Lukáš Rýček's group in ChemistrySelect:

- Publication of a review Jan Veselý's group in Chemical Record:

- Císařová, I.; Holovko-Kamoshenkova, O. M.; Hrdina, R.; Koucký, F.; Machalický, O. Annulated carbamates are precursors for the ring contraction of the adamantane framework. RSC Advances [online] 2022, 12 (48), 31056-31060.
- Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M.; Kráľ, M.; Machara, A.; Majer, P.; Reiberger, R. Bioisosteres of Luteolin: New Class of Potential Inhibitors of Influenza Virus RNA-Polymerase, 2022.
- Bingel, S.; Caivano, I.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M.; Nečas, D. Catalytic approach to unsymmetrical [7]-helical indenofluorenes: Cyclotrimerization vs. dehydro-Diels-Alder reaction pathways. Catalysis Today 2022, 390-391 (May), 48-56.
- Bhosale, V. Anandrao; Císařová, I.; Kamlar, M.; Veselý, J. Catalytic asymmetric addition to cyclic N-acyl-iminium: Access to sulfone-bearing contiguous quaternary stereocenters. Chemical Communications 2022, 58 (71), 9942-9945.
- Čikoš, A.; Degač, M.; Gredičak, M.; Topolovčan, N. Chemoselective and Regioselective Synthesis of Spiroisoindolinone Indenes via an Intercepted Meyer–Schuster Rearrangement/Intramolecular Friedel–Crafts Alkylation Relay. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2022, 87 (5), 3712-3717.
- Asanuma, Y.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M.; Manca, G.; Moss, R.; Ulč, J. Computational, Mechanistic, and Experimental Insights into Regioselective Catalytic C–C Bond Activation in Linear 1-Aza-[3]triphenylene. ACS Omega [online] 2022, 7 (10), 8665-8674.
- Dian, J.; Fourmentin, S.; Jindřich, J.; Palágyi, A. Cyclodextrin-based Schiff base pro-fragrances: Synthesis and release studies. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2022, 18 (September), 1346-1354.
- Císařová, I.; Jacko, J.; Kotora, M.; Rulíšek, L.; Staś, M. Ir-Catalyzed Cycloaddition of Tribenzocyclyne with Biphenylenes. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2022, 87 (1), 744-750.
- Jindřich, J.; Kasal, P. Kinetics of Nucleophilic Substitution of Compounds Containing Multiple Leaving Groups Bound to a Neopentyl Skeleton. ACS Omega [online] 2022, 7 (23), 20137-20144.
- Ausserlechner, M. J.; Dočekal, V.; Hagenbuchner, J.; Horváth, M.; Kaiser, N.; Kohoutová, K.; Mandal, R.; Obšil, T.; Obšilová, V.; Tekel, A.; et al. Lengthening the Guanidine–Aryl Linker of Phenylpyrimidinylguanidines Increases Their Potency as Inhibitors of FOXO3-Induced Gene Transcription. ACS Omega [online] 2022, 7 (38), 34632-34646.
- Ausserlechner, M.; Dočekal, V.; Kohoutová, K.; Obšil, T.; Obšilová, V.; Tekel, A.; Veselý, J. Modulating FOXO3 transcriptional activity by low-molecular compounds. FEBS Open Bio [online], 2022, 12, 233-233.
- Císařová, I.; David, T.; Dračínský, M.; Jirák, D.; Jurok, R.; Kretschmer, J.; Kuchař, M.; Polášek, M.; Socha, O.; Vít, M. Paramagnetic encoding of molecules. Nature Communications [online] 2022, 13 (1), nestránkováno.
- Baszczyňski, O.; Černý, J.; Čmoková, A.; Grobárová, V.; Kolařík, M.; Procházková, E.; Slapničková, M.; Štěpánek, O.; Zíková, A. Piperazine-Modified Ketoconazole Derivatives Show Increased Activity against Fungal and Trypanosomatid Pathogens. ChemMedChem 2022, 17 (21), nestránkováno.
- Hocek, M.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Kodr, D.; Ortiz, M.; O'Sullivan, C. Kathleen; Simonova, A. Solid-phase recombinase polymerase amplification using ferrocene-labelled dNTPs for electrochemical detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2022, 198 (February), nestránkováno.
- Císařová, I.; Dočekal, V.; Gyepes, R.; Hrabovský, J.; Koberová, T.; Rios, R.; Veselý, J.; Vopálenská, A. Stereoselective cyclopropanation of boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) derivatives by an organocascade reaction. Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis 2022, 364 (5), 930-937.
- Bouřa, E.; Dejmek, M.; Chalupská, D.; Klíma, M.; Matoušová, M.; Mertlíková-Kaiserová, H.; Misehe, M.; Nencka, R.; Šála, M. Structure-based design and modular synthesis of novel PI4K class II inhibitors bearing a 4-aminoquinazoline scaffold. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2022, 76 (November), nestránkováno.
- Mateus, M. Alexandre; Kunák, D.; Rýček, L. Synthesis and Structure Confirmation of Selagibenzophenone C. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2022, 2022 (11), nestránkováno.
- Hocek, M.; Ondruš, M.; Sýkorová, V. Traceless enzymatic synthesis of monodispersed hypermodified oligodeoxyribonucleotide polymers from RNA templates. Chemical Communications 2022, 58 (80), 11248-11251.
- Benýšek, J.; Krečmerová, M.; Matoušová, M.; Kaiserová, H. Mertlíkov; Otmar, M.; Pohl, R.; Pomeisl, K.; Pomeislová, A.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Rubešová, P. 1,2,4-Thiadiazole acyclic nucleoside phosphonates as inhibitors of cysteine dependent enzymes cathepsin K and GSK-3β. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 32 (February), nestránkováno.
- Fadeev, A.; Makarov, A. S.; Uchuskin, M. G. Acid-Catalyzed Cascade Reaction of 2-Alkylfurans with α,β-Unsaturated Ketones: A Shortcut to 2,3,5-Trisubstituted Furans. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 86 (23), 17362-17370.
- Břehová, P.; Česnek, M.; Dračínský, M.; Chaloupecká, E.; Janeba, Z.; Mertlíková-Kaiserová, H.; Skácel, J.; Soto-Velasquez, M. P.; Tloušťová, E.; Watts, V. J. Acyclic nucleoside phosphonates with 2-aminothiazole base as inhibitors of bacterial and mammalian adenylate cyclases. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 222 (October 15 2021), nestránkováno.
- Bouřa, E.; Čížek, K.; Eyer, L.; Hocek, M.; Hodek, J.; Konkoľová, E.; Kozák, J.; Milisavljević, N.; Nencka, R.; Pohl, R.; et al. Antiviral Activity of 7-Substituted 7-Deazapurine Ribonucleosides, Monophosphate Prodrugs, and Triphoshates against Emerging RNA Viruses. ACS Infectious Diseases 2021, 7 (2), 471-478.
- Bricout, H.; Caronia, E.; Galia, A.; Tichá, I. Chena; Jindřich, J.; Léger, B.; Menuel, S.; Monflier, É.; Noël, S.; Ponchel, A.; et al. Asymmetric hydrogenation of ethyl pyruvate over aqueous dispersed Pt nanoparticles stabilized by a cinchonidine-functionalized β-cyclodextrin. Catalysis Communications 2021, 150 (February), nestránkováno.
- Fojta, M.; Havran, L.; Hocek, M.; Kodr, D.; Lesnikowski, Z. J.; Ortiz, M.; O'Sullivan, C. Kathleen; Pohl, R.; Saftić, D. Pavlović; Simonova, A.; et al. Carborane- or Metallacarborane-Linked Nucleotides for Redox Labeling. Orthogonal Multipotential Coding of all Four DNA Bases for Electrochemical Analysis and Sequencing. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2021, 143 (18), 7124-7134.
- Beytlerová, N.; Mateus, M. Alexandre; Kotora, M.; Rýček, L. Catalytic Cyclotrimerization Pathway for Synthesis of Selaginpulvilins C and D: Scope and Limitations. Organic Letters 2021, 23 (12), 4511-4515.
- Groborz, O.; Holubová, M.; Hromádková, J.; Hrubý, M.; Lobaz, V.; Loukotová, L.; Pechrová, Z.; Rabyk, M.; Štěpánek, P.; Trhlíková, O. Chemically modified glycogens: How they influence formation of amyloid fibrils?. Soft Matter 2021, 17 (6), 1614-1627.
- Mateus, M. Alexandre; Lapinskaite, R.; Malatinec, Š.; Rýček, L. Cross-Coupling as a Key Step in the Synthesis and Structure Revision of the Natural Products Selagibenzophenones A and B. Catalysts [online] 2021, 11 (6), nestránkováno.
- Čihák, M.; Hurný, D.; Malečková, A.; Štuka, Č.; Tonar, Z.; Vejražka, M. "Desatero" akademického pedagoga. https://karlovkaonline.cz/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/UK_fond-desatero_www.pdf, 2021.
- Bělinová, T.; Beneš, H.; Groborz, O.; Heizer, T.; Herynek, V.; Hrubý, M.; Loukotová, L.; Raabová, H.; Švec, P. Direct Comparison of Analogous Amphiphilic Gradient and Block Polyoxazolines. Macromolecules 2021, 54 (17), 8182-8194.
- Baszczyňski, O.; Dračínský, M.; Dvořáková, A.; Hodek, J.; Chalupský, K.; Janeba, Z.; Kalčic, F.; Kaiserová, H. Mertlíkov; Strmeň, T.; Šebestík, J.; et al. Discovery of Modified Amidate (ProTide) Prodrugs of Tenofovir with Enhanced Antiviral Properties. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 64 (22), 16425-16449.
- Dračínský, M.; Drastík, M.; Kašpar, M.; Klepetářová, B.; Kronenberger, T.; Kudová, E.; Mičuda, S.; Pávek, P.; Štefela, A. (E)-7-Ethylidene-lithocholic Acid (7-ELCA) Is a Potent Dual Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Antagonist and GPBAR1 Agonist Inhibiting FXR-Induced Gene Expression in Hepatocytes and Stimulating Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion From Enteroendocrine Cells. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2021, 12 (August), nestránkováno.
- Císařová, I.; Géant, P. Yves; Kamlar, M.; Remeš, M.; Šotolová, M.; Štícha, M.; Veselý, J. Enantioselective Organocatalytic Synthesis of 1,2,3-Trisubstituted Cyclopentanes. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 2021 (36), 5080-5089.
- Císařová, I.; Kamlar, M.; Nigríni, M.; Reiberger, R.; Veselý, J. Enantioselective PCCP Brønsted acid-catalyzed aminalization of aldehydes. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 17 (September), 2433-2440.
- Kamlar, M.; Sunden, H.; Zacharias, S. C. Exploring Supramolecular Gels in Flow-Type Chemistry-Design and Preparation of Stationary Phases. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research 2021, 60 (28), 10056-10063.
- Forster, R. J.; Hocek, M.; Magriñá, I.; Ortiz, M.; O'Sullivan, C. Kathleen; Simonova, A. Ferrocene-Containing DNA Monolayers: Influence of Electrostatics on the Electron Transfer Dynamics. Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids 2021, 37 (11), 3359-3369.
- Beier, P.; Chvojka, T.; Janecký, L.; Klepetářová, B.; Markos, A.; Martínek, T.; Martinez-Seara, H. Haloalkenyl Imidoyl Halides as Multifacial Substrates in the Stereoselective Synthesis of N-Alkenyl Compounds. Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis 2021, 363 (13), 3258-3266.
- Bednářová, E.; Kotora, M.; Malatinec, Š.; Tanaka, H. Highly Enantioselective Ring-Opening of meso-Epoxides with O- and N-Nucleophiles Catalyzed by a Chiral Sc(III)/bipyridine Complex. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 2021 (8), 1249-1257.
- Fadeev, A.; Makarov, A. S.; Uchuskin, M. G. Intramolecular iron-catalyzed transannulation of furans with O-acetyl oximes: synthesis of functionalized pyrroles. Organic Chemistry Frontiers 2021, 8 (23), 6553-6560.
- Bourassi, M.; Gaálová, J.; Izák, P.; Jindřich, J.; Kasal, P.; Ladewig, B. P.; Michel, M. Nafion membranes modified by cationic cyclodextrin derivatives for enantioselective separation. Separation and Purification Technology 2021, 266 (July), nestránkováno.
- Baszczyňski, O.; Císařová, I.; Flieger, M.; Kolařík, M.; Kucherak, O.; Procházková, E.; Stodůlková, E.; Tošner, Z. NMR Structure Elucidation of Naphthoquinones from Quambalaria cyanescens. Journal of Natural Products 2021, 84 (1), 46-55.
- Gallardo, P. Güixens; Hocek, M.; Kraus, T.; Kuba, M.; Matyašovský, J.; Palágyi, A.; Pohl, R.; Tack, L. Nucleotides bearing aminophenyl- or aminonaphthyl-3-methoxychromone solvatochromic fluorophores for the enzymatic construction of DNA probes for the detection of protein-DNA binding. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 2021, 19 (45), 9966-9974.
- Baszczyňski, O.; Cigáň, M.; Filo, J.; Májek, M.; Procházková, E.; Straka, M.; Šimon, P. Phosphate linkers with traceable cyclic intermediates for self-immolation detection and monitoring. Chemical Communications 2021, 57 (2), 211-214.
- Baszczyňski, O.; Gallardo, M. García; Procházková, E.; Šimon, P.; Tichotová, M. Phosphate-Based Self-Immolative Linkers for Tuneable Double Cargo Release. Chemistry - A European Journal 2021, 27 (50), 12763-12775.
- Kočovský, P.; Kuneš, J.; Kysilka, O.; Májek, M.; Maříková, J.; Matouš, P.; Pour, M.; Růžička, A. Reaction Outcome Critically Dependent on the Method of Workup: An Example from the Synthesis of 1-Isoquinolones. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 86 (12), 8078-8088.
- Beier, P.; Janecký, L.; Klepetářová, B.; Markos, A.; Pohl, R. Stereoselective synthesis of (Z)-β-enamido fluorides from N-fluoroalkyl- and N-sulfonyl-1,2,3-triazoles. Organic Letters 2021, 23 (11), 4224-4227.
- Hejdánek, J.; Hodek, J.; Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M.; Machara, A.; Pachl, P.; Radilová, K.; Řezáčová, P.; Weber, J. Structural characterization of the interaction between the C-terminal domain of the influenza polymerase PA subunit and an optimized small peptide inhibitor. Antiviral Research 2021, 185 (January), nestránkováno.
- Doleželová, E.; Downey, A. Michael; Hocek, M.; Nguyen, V. Hai; Pohl, R.; Rožánková, S.; Slapničková, M.; Tichý, M.; Tloušťová, E.; Zíková, A. Synthesis and anti-trypanosomal activity of 3'-fluororibonucleosides derived from 7-deazapurine nucleosides. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2021, 40 (May 15 2021), nestránkováno.
- Doleželová, E.; Džubák, P.; Gurská, S.; Hajdúch, M.; Hocek, M.; Krajczyk, A.; Milisavljević, N.; Perlíková, P.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Slapničková, M.; et al. Synthesis and Antitrypanosomal Activity of 6-Substituted 7-Methyl-7-deazapurine Nucleosides. ACS Infectious Diseases 2021, 7 (4), 917-926.
- Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M.; Kráľ, M.; Machara, A.; Majer, P.; Radilová, K.; Reiberger, R. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of C-7 and C-8 Luteolin Derivatives as Influenza Endonuclease Inhibitors, 2021.
- Císařová, I.; Henriksson, E.; Kamlar, M.; Malo, M.; Sunden, H. Synthesis of cis-Oriented Vicinal Diphenylethylenes through a Lewis Acid-Promoted Annulation of Oxotriphenylhexanoates. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 86 (13), 8660-8671.
- Bažíková, E.; Císařová, I.; Jagtap, P. Ramling; Matoušová, E.; Nechaev, A.; Neumannová, J. Synthesis of fused 1,2-naphthoquinones with cytotoxic activity using a one-pot three-step reaction. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 2021, 19 (15), 3434-3440.
- Bakhanovich, O.; Beier, P.; Khutorianskyi, V.; Motornov, V. Synthesis of N-perfluoroalkyl-3,4-disubstituted pyrroles by rhodium-catalyzed transannulation of N-fluoroalkyl-1,2,3-triazoles with terminal alkynes. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2021, 17 (February 18 2021), 504-510.
- Hurný, D.; Malečková, A.; Štuka, Č.; Tonar, Z.; Vejražka, M. Ten evidence-based recommendations for higher education. Mefanet+ 2021: Cooperation on the effective use of technology in medical and healthcare education reflecting on the challenges of today, 2021, 13-13.
- Brábek, J.; Černochová, Z.; Groborz, O.; Hrubý, M.; Kolouchová, K.; Rösel, D.; Starčuk, Z.; Škarková, A.; Šlouf, M.; Švec, P. Thermo- and ROS-Responsive Self-Assembled Polymer Nanoparticle Tracers for F-19 MRI Theranostics. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22 (6), 2325-2337.
- Catanzano, O.; Conte, C.; Fraix, A.; Kalydi, E.; Kasal, P.; Payamifar, S.; Quaglia, F.; Seggio, M.; Sortino, S. Visible light-activatable cyclodextrin-conjugates for the efficient delivery of nitric oxide with fluorescent reporter and their inclusion complexes with betaxolol. New Journal of Chemistry 2021, 45 (19), 8449-8455.
- Brunderová, M.; Hocek, M.; Ivancova, I.; Krömer, M.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová. 2-Formyl-dATP as Substrate for Polymerase Synthesis of Reactive DNA Bearing an Aldehyde Group in the Minor Groove. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85 (6), 1164-1170 DOI: 10.1002/cplu.202000287.
- Hocek, M.; Matyašovský, J. 2-Substituted 2 '-deoxyinosine 5 '-triphosphates as substrates for polymerase synthesis of minor-groove-modified DNA and effects on restriction endonuclease cleavage. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 2020, 18 (2), 255-262 DOI: 10.1039/c9ob02502b.
- Drastík, M.; Holas, O.; Hroch, M.; Hutníková, M.; Kašpar, M.; Kudová, E.; Mičuda, S.; Pandey, A. V.; Pávek, P.; Smutný, T.; et al. 3 beta-Isoobeticholic acid efficiently activates the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) due to its epimerization to 3 alpha-epimer by hepatic metabolism. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2020, 202 (September), nestránkováno DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105702.
- Císařová, I.; Formánek, B.; Tauchman, J.; Vesely, J. Access to Spirocyclic Benzothiophenones with Multiple Stereocenters via an Organocatalytic Cascade Reaction. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 85 (13), 8510-8521 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00882.
- Bednářová, E.; Kotora, M.; Malatinec, Š. Applications of Bolm's Ligand in Enantioselective Synthesis. Molecules 2020, 25 (4), nestránkováno DOI: 10.3390/molecules25050958.
- Brynda, J.; Fanfrlík, J.; Hadzima, M.; Hánová, I.; Horn, M.; Houštecká, R.; Lepšík, M.; Majer, P.; Mareš, M.; Mertlíková-Kaiserová, H.; et al. Biomimetic Macrocyclic Inhibitors of Human Cathepsin D: Structure-Activity Relationship and Binding Mode Analysis. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 63 (4), 1576-1596 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01351.
- Báječný, M.; Beneš, J.; Czernek, J.; Dunlop, D.; Francová, P.; Groborz, O.; Heizer, T.; Hobza, P.; Hrubý, M.; Kolouchová, K.; et al. Chelating Polymers for Hereditary Hemochromatosis Treatment. Macromolecular Bioscience 2020, 20 (12), nestránkováno DOI: 10.1002/mabi.202000254.
- Kasireddy, S. Reddy; Míšek, J.; Nosek, V.; Tarallo, V. Development of a simple high-throughput assay for directed evolution of enantioselective sulfoxide reductases. Chemical Communications 2020, 56 (40), 5386-5388 DOI: 10.1039/d0cc01660h.
- Císařová, I.; Docekal, V.; Petrželová, S.; Vesely, J. Enantioselective Cyclopropanation of 4-Nitroisoxazole Derivatives. Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis 2020, 362 (13), 2597-2603 DOI: 10.1002/adsc.202000231.
- Bultel-Ponce, V.; Durand, T.; Galano, J. - M.; Guy, A.; Jahn, U.; Oger, C.; Pavlíčková, T.; Reversat, G.; Rocher, A.; Vigor, C. First Total Syntheses of Novel Non-Enzymatic Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Metabolites and Their Identification in Edible Oils. Chemistry - A European Journal 2020, 26 (44), 10090-10098 DOI: 10.1002/chem.202002138.
- Caivano, I.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M.; Nečas, D.; Tošner, Z. A General Synthetic Approach and Photophysical Properties of Regioselectively Fluorinated [5]- and [6]-Helical Bispiroindenofluorenes. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85 (9), 2010-2016 DOI: 10.1002/cplu.202000434.
- Gálisová, A.; Groborz, O.; Hájek, M.; Hrubý, M.; Jirák, D.; Kolouchová, K.; Sedláček, O.; Sticová, E.; Švec, P.; Trousil, J.; et al. Implant-forming polymeric 19F MRI-tracer with tunable dissolution. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 327 (November), 50-60 DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.026.
- Bušek, P.; Konvalinka, J.; Šedo, A.; Šimková, A. Molecular recognition of fibroblast activation protein for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Proteins and Proteomics 2020, 1868 (7), nestránkováno DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140409.
- Anania, M.; Jašík, J.; Jašíková, L.; Roithová, J.; Shcherbachenko, E.; Zelenka, J. Monoaurated vs. diaurated intermediates: causality or independence?. Chemical Science 2020, 11 (4), 980-988 DOI: 10.1039/c9sc05662a.
- Barek, J.; Klouda, J.; Kočovský, P.; Nesměrák, K.; Schwarzova-Peckova, K. A novel voltammetric approach to the detection of primary bile acids in serum samples. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 134 (August), nestránkováno DOI: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107539.
- Kadaník, M.; Kočovský, P.; Kuneš, J.; Maříková, J.; Matouš, P.; Pour, M.; Růžička, A.; Timoracký, M. Nucleophile-assisted cyclization of beta-propargylamino acrylic compounds catalyzed by gold(I): a rapid construction of multisubstituted tetrahydropyridines and their fused derivatives. Organic Chemistry Frontiers 2020, 7 (21), 3356-3367 DOI: 10.1039/d0qo00653j.
- Brown, T.; El-Sagheer, A. H.; Hocek, M.; Kellett, A.; Panattoni, A. Oxidative DNA Cleavage with Clip-Phenanthroline Triplex-Forming Oligonucleotide Hybrids. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2020, 21 (7), 991-1000 DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201900670.
- Hausnerova, V. Vankova; Hocek, M.; Chakrapani, A.; Krásný, L.; Pohl, R.; Ruiz-Larrabeiti, O. Photocaged 5-(Hydroxymethyl)pyrimidine Nucleoside Phosphoramidites for Specific Photoactivatable Epigenetic Labeling of DNA. Organic Letters 2020, 22 (22), 9081-9085 DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03462.
- Beier, P.; Klimánková, I.; Košťál, V.; Motornov, V.; Tichy, D. Preparation of 1-Azido-2-Bromo-1,1,2,2-Tetrafluoroethane and Its Use in the Synthesis of N-Fluoroalkylated Nitrogen Heterocycles. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 85 (17), 11482-11489 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c01610.
- Džubák, P.; Gurska, S.; Hajdúch, M.; Hocek, M.; Pohl, R.; Tloušťová, E.; Veselovská, L. Pyrido-Fused Deazapurine Bases: Synthesis and Glycosylation of 4-Substituted 9H-Pyrido[2',3':4,5]- and Pyrido[4',3':4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines. ACS Omega [online] 2020, 5 (40), 26278-26286 DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04302.
- Bastien, G.; Císařová, I.; Dračínský, M.; Hurtado, C. Santos; Kaleta, J.; Mašát, M.; Rogers, C. T.; Rončević, I.; Štoček, J. Radek. Regular Two-Dimensional Arrays of Surface-Mounted Molecular Switches: Switching Monitored by UV-vis and NMR Spectroscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2020, 142 (20), 9337-9351 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c01753.
- Abdelsayed, M. M.; A. Chamberlin, R.; Chizzolini, F.; Kasireddy, S. Reddy; Luptak, A.; Míšek, J.; Passalacqua, L. F. M.; Rotstan, K. A. Regulation of mRNA translation by a photoriboswitch. eLife 2020, 9 (February 2020), nestránkováno DOI: 10.7554/eLife.51737.
- Bursová, M.; Čabala, R.; Hložek, T.; Jelinek, I.; Štícha, M.; Tůma, P. Sensitive CE-MS method for monitoring of riociguat and desmethylriociguat levels in human serum. Electrophoresis 2020, 41 (18-19), 1564-1567 DOI: 10.1002/elps.202000135.
- Baszczynski, O.; Cigáň, M.; Filo, J.; Prochazkova, E. Sterically-Controlled Self-Immolation in Phosphoramidate Linkers Triggered by Light. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 2020 (7), 897-906 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201901882.
- Císařová, I.; Hara, S.; Kotora, M.; Topolovčan, N.; Tošner, Z. A Study of Polarization and Directing Effects of Unsymmetrical Alkynes Using Regioselective Pd-Catalyzed Bromoallylation. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 2020 (2), 234-240 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201901476.
- Brynda, J.; Das, V.; Dvořanová, J.; Džubák, P.; Anwar, S. El; Fábry, M.; Grüner, B.; Gurska, S.; Hajdúch, M.; Havránek, M.; et al. Sulfonamido carboranes as highly selective inhibitors of cancer-specific carbonic anhydrase IX. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 200 (August), nestránkováno DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112460.
- Bartova, K.; Džubák, P.; Fleuti, M. Heidi; Gurska, S.; Hajdúch, M.; Hocek, M.; Pavliš, P.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Tichý, M.; Tloušťová, E. Synthesis and Biological Profiling of Pyrazolo-Fused 7-Deazapurine Nucleosides. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 85 (16), 10539-10551 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00928.
- Džubák, P.; Gurska, S.; Hajdúch, M.; Hocek, M.; Pavliš, P.; Pohl, R.; Tichý, M.; Yang, C. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, and Biological Profiling of Benzothieno-Fused 7-Deazapurine Ribonucleosides. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 85 (12), 8085-8101 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00927.
- Bakhanovich, O.; Beier, P. Synthesis, Stability and Reactivity of alpha-Fluorinated Azidoalkanes. Chemistry - A European Journal 2020, 26 (4), 773-782 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201903627.
- Gallardo, P. Güixens; Hocek, M.; Hof, M.; Humpolickova, J.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Kraus, T.; Miclea, S. Paul; Pohl, R. Thiophene-linked tetramethylbodipy-labeled nucleotide for viscosity-sensitive oligonucleotide probes of hybridization and protein-DNA interactions. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 2020, 18 (5), 912-919 DOI: 10.1039/c9ob02634g.
- Albiñana, C. Berenguer; Brynda, J.; Fanfrlík, J.; Flieger, M.; Hodek, J.; Karlukova, E.; Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M.; Machara, A.; Majer, P.; et al. Unraveling the anti-influenza effect of flavonoids: Experimental validation of luteolin and its congeners as potent influenza endonuclease inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 208 (December), nestránkováno DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112754.
- Fojta, M.; Havran, L.; Havranova-Vidlakova, P.; Hocek, M.; Krömer, M.; Sykorova, V.; Trefulka, M. Vicinal Diol-Tethered Nucleobases as Targets for DNA Redox Labeling with Osmate Complexes. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2020, 21 (1-2), 171-180 DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201900388.
- Terencio, T.; Andris, E.; Gamba, I.; Srnec, M.; Costas, M.; Roithová, J. Chemoselectivity in the Oxidation of Cycloalkenes with a Non-Heme Iron(IV)-Oxo-Chloride Complex: Epoxidation vs. Hydroxylation Selectivity. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2019, 30 (10), 1923-1933 DOI: 10.1007/s13361-019-02251-1.
- Franc, M.; Urban, M.; Císařová, I.; Vesely, J. Highly enantioselective addition of sulfur-containing heterocycles to isatin-derived ketimines. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2019, 17 (31), 7309-7314 DOI: 10.1039/c9ob01338e.
- Tarallo, V.; Kasireddy, S.; Misek, J. In vitro evolution of sulfoxide reductases. Journal of Biotechnology 2019, 305, S30-S30 DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.05.113.
- Ticha, I. Chena; Hybelbauerová, S.; Jindřich, J. New alpha- and beta-cyclodextrin derivatives with cinchona alkaloids used in asymmetric organocatalytic reactions. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2019, 15, 830-839 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.15.80.
- Prochazkova, E.; Navrátil, R.; Janeba, Z.; Roithová, J.; Baszczynski, O. Reactive cyclic intermediates in the ProTide prodrugs activation: trapping the elusive pentavalent phosphorane. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2019, 17 (2), 315-320 DOI: 10.1039/c8ob02870b.
- Kulkarni, R.; Noda, Y.; Barange, D. Kumar; Kochergin, Y. S.; Lyu, P.; Balcarova, B.; Nachtigall, P.; Bojdys, M. J. Real-time optical and electronic sensing with a beta-amino enone linked, triazine-containing 2D covalent organic framework. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 3228 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11264-z.
- Ivancova, I.; Pohl, R.; Hubalek, M.; Hocek, M. Squaramate-Modified Nucleotides and DNA for Specific Cross-Linking with Lysine-Containing Peptides and Proteins. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2019, 58 (38), 13345-13348 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201906737.
- Markos, A.; Voltrova, S.; Motornov, V.; Tichy, D.; Klepetářová, B.; Beier, P. Stereoselective Synthesis of (Z)-beta-Enamido Triflates and Fluorosulfonates from N-Fluoroalkylated Triazoles. Chemistry-a European Journal 2019, 25 (32), 7640-7644 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201901632.
- Malnuit, V.; Smolen, S.; Tichý, M.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Hocek, M. Synthesis of Cyclic and Acyclic Nucleoside Phosphonates and Sulfonamides Derived from 6-(Thiophen-2-yl)-7-fluoro-7-deazapurine. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2019, 2019 (31-32), 5409-5423 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201900509.
- Gerlich, D.; Jašík, J.; Roithová, J. Tagging fullerene ions with helium in a cryogenic quadrupole trap. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2019, 438, 78-86 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijms.2018.12.018.
- Havranova-Vidlakova, P.; Kroemer, M.; Sykorova, V.; Trefulka, M.; Fojta, M.; Havran, L.; Hocek, M. Vicinal Diol-Tethered Nucleobases as Targets for DNA Redox Labeling with Osmate Complexes. Chembiochem 2019 DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201900388.
- Matyašovský, J.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. 2-Allyl- and Propargylamino-dATPs for Site-Specific Enzymatic Introduction of a Single Modification in the Minor Groove of DNA. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24 (56), 14938-14941 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803973.
- Güixens-Gallardo, P.; Zawada, Z.; Matyašovský, J.; Dziuba, D.; Pohl, R.; Kraus, T.; Hocek, M. Brightly Fluorescent 2 '-Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphates Bearing Methylated Bodipy Fluorophore for in Cellulo Incorporation to DNA, Imaging, and Flow Cytometry. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2018, 29 (11), 3906-3912 DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00721.
- Bris, A.; Turel, I.; Roithová, J. C-H Bond Activation by a Ruthenium(II) beta-Diketonate Complex: A Mechanistic Study. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2018, No. 44, 6107-6113 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201800787.
- Sabat, N.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. C-H Imidation of 7-Deazapurines. Acs Omega 2018, 3 (4), 4674-4678 DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b00520.
- Nosek, V.; Míšek, J. Chemoenzymatic Deracemization of Chiral Sulfoxides. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2018, 57 (31), 9849-9852 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201805858.
- Ulč, J.; Nečas, D.; Koukal, P.; Havlicek, V.; Tošner, Z.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Kotora, M. Chiral Unsymmetrically Substituted Bipyridine N,N-Dioxides as Catalysts for the Allylation of Aldehydes. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2018, No. 37, 5109-5116 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201800485.
- Docekal, V.; Šimek, M.; Dračínský, M.; Vesely, J. Decarboxylative Organocatalytic Allylic Amination of Morita-Baylis-Hillman Carbamates. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24 (51), 13441-13445 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803677.
- Andris, E.; Navrátil, R.; Jašík, J.; Sabenya, G.; Costas, M.; Srnec, M.; Roithová, J. Detection of Indistinct Fe-N Stretching Bands in Iron(V) Nitrides by Photodissociation Spectroscopy. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24 (20), 5078-5081 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201705307.
- Makukhin, N.; Nosek, V.; Míšek, J. Development of a Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe with Two Reactive Sulfoxides for Monitoring the Activity of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A. Synthesis-Stuttgart 2018, 50 (4), 772-777 DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1591888.
- Kaiser, R. P.; Ulc, J.; Císařová, I.; Necas, D. Direct regioselective C-H borylation of [5]helicene. Rsc Advances 2018, 8 (1), 580-583 DOI: 10.1039/c7ra13021j.
- Mikušek, J.; Jansa, P.; Jagtap, P. R.; Vasicek, T.; Císařová, I.; Matoušová, E. Enantioselective Synthesis of All-Carbon Quaternary Centers Structurally Related to Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24 (40), 10069-10072 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201802493.
- Srnec, M.; Navrátil, R.; Andris, E.; Jašík, J.; Roithová, J. Experimentally Calibrated Analysis of the Electronic Structure of CuO+: Implications for Reactivity. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2018, 57 (52), 17053-17057 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201811362.
- Kochergin, Y. S.; Schwarz, D.; Acharjya, A.; Ichangi, A.; Kulkarni, R.; Eliasova, P.; Vacek, J.; Schmidt, J.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys, M. J. Exploring the "Goldilocks Zone" of Semiconducting Polymer Photocatalysts by Donor-Acceptor Interactions. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2018, 57 (43), 14188-14192 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201809702.
- Schwarz, D.; Acharja, A.; Ichangi, A.; Lyu, P.; Opanasenko, M. V.; Gossler, F. R.; Konig, T. A. F.; Cejka, J.; Nachtigall, P.; Thomas, A.; et al. Fluorescent Sulphur- and Nitrogen-Containing Porous Polymers with Tuneable Donor-Acceptor Domains for Light-Driven Hydrogen Evolution. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24 (46), 11916-11921 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201802902.
- Ghosh, K.; Perlíková, P.; Havlicek, V.; Yang, C.; Pohl, R.; Tloušťová, E.; Hodek, J.; Gurska, S.; Džubák, P.; Hajdúch, M.; et al. Isomeric Naphtho-Fused 7-Deazapurine Nucleosides and Nucleotides: Synthesis, Biological Activity, Photophysical Properties and Enzymatic Incorporation to Nucleic Acids. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2018, No. 37, 5092-5108 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201800165.
- Strelnikov, D.; Jašík, J.; Gerlich, D.; Murata, M.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Roithová, J. Near- and Mid-IR Gas-Phase Absorption Spectra of H-2@C-60(+)-He. Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2018, 122 (41), 8162-8166 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.8b06222.
- Krömer, M.; Bartova, K.; Raindlová, V.; Hocek, M. Synthesis of Dihydroxyalkynyl and Dihydroxyalkyl Nucleotides as Building Blocks or Precursors for Introduction of Diol or Aldehyde Groups to DNA for Bioconjugations. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24 (46), 11890-11894 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201802282.
- Andris, E.; Navrátil, R.; Jašík, J.; Puri, M.; Costas, M.; Que, L.; Roithová, J. Trapping Iron(III)-Oxo Species at the Boundary of the "Oxo Wall": Insights into the Nature of the Fe(III)-O Bond. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2018, 140 (43), 14391-14400 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b08950.
- Janoušková, M.; Vaníková, Z.; Nici, F.; Boháčová, S.; Vitovska, D.; Šanderová, H.; Hocek, M.; Krásný, L. 5-(Hydroxymethyl) uracil and -cytosine as potential epigenetic marks enhancing or inhibiting transcription with bacterial RNA polymerase. Chemical Communications 2017, 53 (99), 13253-13255 DOI: 10.1039/c7cc08053k.
- Roeser, J.; Prill, D.; Bojdys, M. J.; Fayon, P.; Trewin, A.; Fitch, A. N.; Schmidt, M. U.; Thomas, A. Anionic silicate organic frameworks constructed from hexacoordinate silicon centres. Nature Chemistry 2017, 9 (10), 977-982 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2771.
- Kamlar, M.; Císařová, I.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Vesely, J. Asymmetric Allylic Amination of Morita-Baylis-Hillman Carbonates with Silylated tert-Butylhydroxycarbamate Derivatives. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2017, No. 14, 1926-1930 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201700222.
- Balintová, J.; Simonova, A.; Bialek-Pietras, M.; Olejniczak, A.; Lesnikowski, Z. J.; Hocek, M. Carborane-linked 2 '-deoxyuridine 5 '-O-triphosphate as building block for polymerase synthesis of carborane-modified DNA. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2017, 27 (21), 4786-4788 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.09.064.
- Fejos, I.; Varga, E.; Benkovics, G.; Malanga, M.; Sohajda, T.; Szeman, J.; Beni, S. Characterization of a single-isomer carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin in chiral capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2017, 38 (15), 1869-1877 DOI: 10.1002/elps.201700004.
- Andris, E.; Navrátil, R.; Jašík, J.; Terencio, T.; Srnec, M.; Costas, M.; Roithová, J. Chasing the Evasive Fe = O Stretch and the Spin State of the Iron(IV)-Oxo Complexes by Photodissociation Spectroscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2017, 139 (7), 2757-2765 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b12291.
- Urban, M.; Franc, M.; Hofmanova, M.; Císařová, I.; Veselý, J. The enantioselective addition of 1-fluoro-1-nitro (phenylsulfonyl) methane to isatin-derived ketimines. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2017, 15 (43), 9071-9076 DOI: 10.1039/c7ob02408h.
- Dian, J.; Jindřich, J.; Jelinek, I. Functionalized materials with fluorescent dyes for chemosensor applications. Monatshefte Fur Chemie 2017, 148 (11), 1929-1935 DOI: 10.1007/s00706-017-2041-6.
- Kopecna, M.; Machacek, M.; Prchalová, E.; Stepanek, P.; Drasar, P.; Kotora, M.; Vavrova, K. Galactosyl Pentadecene Reversibly Enhances Transdermal and Topical Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutical Research 2017, 34 (10), 2097-2108 DOI: 10.1007/s11095-017-2214-3.
- Zhang, K.; Meazza, M.; Docekal, V.; Light, M. E.; Vesely, J.; Rios, R. Highly Diastereo- and Enantioselective Synthesis of alpha-Spiro-delta-lactams by an Organocascade Reaction. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2017, No. 13, 1749-1756 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201700193.
- Trautner, S.; Jašík, J.; Parigger, C. G.; Pedarnig, J. D.; Spendelhofer, W.; Lackner, J.; Veis, P.; Heitz, J. Laser-induced optical breakdown spectroscopy of polymer materials based on evaluation of molecular emission bands. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2017, 174, 331-338 DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.11.045.
- Trautner, S.; Jašík, J.; Parigger, C. G.; Pedarnig, J. D.; Spendelhofer, W.; Lackner, J.; Veis, P.; Heitz, J. Laser-induced optical breakdown spectroscopy of polymer materials based on evaluation of molecular emission bands (vol 174, pg 331, 2017). Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2017, 179, 73-73 DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.02.016.
- Benkovics, G.; Afonso, D.; Darcsi, A.; Beni, S.; Conoci, S.; Fenyvesi, E.; Szente, L.; Malanga, M.; Sortino, S. Novel beta-cyclodextrin-eosin conjugates. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2017, 13, 543-551 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.13.52.
- Yassaghi, G.; Andris, E.; Roithová, J. Reactivity of Copper(III)-Oxo Complexes in the Gas Phase. Chemphyschem 2017, 18 (16), 2217-2224 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201700490.
- Váňa, J.; Lang, J.; Soltesova, M.; Hanusek, J.; Růžička, A.; Sedlák, M.; Roithová, J. The role of trinuclear species in a palladium acetate/trifluoroacetic acid catalytic system. Dalton Transactions 2017, 46 (46), 16269-16275 DOI: 10.1039/c7dt03832a.
- Araki, Y.; Topolovčan, N.; Kotora, M. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Cross-Metathesis of Allyl Acetate and Styrenes: A Practical Approach to the Synthesis of Tripolinolate A and Its Analogs. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2017, No. 13, 1736-1739 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201700132.
- Andris, E.; Navrátil, R.; Jašík, J.; Sabenya, G.; Costas, M.; Srnec, M.; Roithová, J. Spin-State-Controlled Photodissociation of Iron(III) Azide to an Iron(V) Nitride Complex. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2017, 56 (45), 14057-14060 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201707420.
- A. Downey, M.; Pohl, R.; Roithová, J.; Hocek, M. Synthesis of Nucleosides through Direct Glycosylation of Nucleobases with 5-O-Monoprotected or 5-Modified Ribose: Improved Protocol, Scope, and Mechanism. Chemistry-a European Journal 2017, 23 (16), 3910-3917 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201604955.
- Kaiser, R. P.; Mosinger, J.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M. Synthesis of selectively 4-substituted 9,9 '-spirobifluorenes and modulation of their photophysical properties. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2017, 15 (33), 6913-6920 DOI: 10.1039/c7ob01319a.
- Schwarz, D.; Kochergin, Y. S.; Acharjya, A.; Ichangi, A.; Opanasenko, M. V.; Cejka, J.; Lappan, U.; Arki, P.; He, J.; Schmidt, J.; et al. Tailored Band Gaps in Sulfur- and Nitrogen-Containing Porous Donor-Acceptor Polymers. Chemistry-a European Journal 2017, 23 (53), 13023-13027 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201703332.
- Schwarz, D.; Noda, Y.; Klouda, J.; Schwarzova-Peckova, K.; Tarabek, J.; Rybacek, J.; Janousek, J.; Simon, F.; Opanasenko, M. V.; Cejka, J.; et al. Twinned Growth of Metal-Free, Triazine-Based Photocatalyst Films as Mixed-Dimensional (2D/3D) van der Waals Heterostructures. Advanced Materials 2017, 29 (40), 1703399 DOI: 10.1002/adma.201703399.
- Benkovics, G.; Malanga, M.; Fenyvesi, E. The 'Visualized' macrocycles: Chemistry and application of fluorophore tagged cyclodextrins. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2017, 531 (2), 689-700 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.04.035.
- Motloch, P.; Blahut, J.; Císařová, I.; Roithová, J. X-ray characterization of triphenylphosphine-gold(I) olefin pi-complexes and the revision of their stability in solution. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 2017, 848, 114-117 DOI: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2017.07.011.
- Matoušová, E.; Gyepes, R.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M. [2+2+2]-Cyclotrimerization of 1-Cyclopropyl-1,6-diynes with Alkynes: Formation of Cyclopropylarenes. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2016, 358 (2), 254-267 DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201500851.
- Bojdys, M. J. 2D or not 2D-Layered Functional (C, N) Materials “Beyond Silicon and Graphene”. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 2016, 217 (2), 232-241 DOI: 10.1002/macp.201500312.
- Matyašovský, J.; Perlíková, P.; Malnuit, V.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. 2-Substituted dATP Derivatives as Building Blocks for Polymerase-Catalyzed Synthesis of DNA Modified in the Minor Groove. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2016, 55 (51), 15856-15859 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201609007.
- Cahová, H.; Panattoni, A.; Kielkowski, P.; Fanfrlík, J.; Hocek, M. 5-Substituted Pyrimidine and 7-Substituted 7-Deazapurine dNTPs as Substrates for DNA Polymerases in Competitive Primer Extension in the Presence of Natural dNTPs. ACS Chemical Biology 2016, 11 (11), 3165-3171 DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00714.
- Bosáková, A.; Perlíková, P.; Tichý, M.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. 6-Aryl-4-amino-pyrimido[4,5-b]indole 2′-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (benzo-fused 7-deaza-dATP analogues): Synthesis, fluorescent properties, enzymatic incorporation into DNA and DNA-protein binding study. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 24 (19), 4528-4535 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.07.054.
- Perlikova, P.; Rylova, G.; Naus, P.; Elbert, T.; Tloustova, E.; Bourderioux, A.; Slavetinska, L. P.; Motyka, K.; Dolezal, D.; Znojek, P.; et al. 7-(2-Thienyl)-7-Deazaadenosine (AB61), a New Potent Nucleoside Cytostatic with a Complex Mode of Action. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2016, 15 (5), 922-937 DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0933.
- Slavíčková, M.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Additions of Thiols to 7-Vinyl-7-deazaadenine Nucleosides and Nucleotides. Synthesis of Hydrophobic Derivatives of 2′-Deoxyadenosine, dATP and DNA. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 81 (22), 11115-11125 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b02098.
- Topolovčan, N.; Panov, I.; Kotora, M. Bisallylation of Zirconacyclopentenes and Ring-Closing Metathesis: A Route to Eight-Membered-Ring Compounds. Synlett 2016, 27 (03), 432-436 DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1560587.
- Pickard, C. J.; Salamat, A.; Bojdys, M. J.; Needs, R. J.; McMillan, P. F. Carbon nitride frameworks and dense crystalline polymorphs. Physical Review B 2016, 94 (9) DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.94.094104.
- Olszewska, A.; Pohl, R.; Brázdová, M.; Fojta, M.; Hocek, M. Chloroacetamide-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Cross-Linking with Peptides and Proteins. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2016, 27 (9), 2089-2094 DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00342.
- Kučerová, G.; Kalíková, K.; Procházková, H.; Popr, M.; Jindřich, J.; Coufal, P.; Tesařová, E. Chromatographic Characterization of a New Cationic β-CD Based Stationary Phase Prepared by Dynamic Coating. Chromatographia 2016, 79 (9-10), 529-536 DOI: 10.1007/s10337-016-3050-z.
- Gerlich, D.; Jašík, J.; Andris, E.; Navrátil, R.; Roithová, J. Collisions of FeO + with H 2 and He in a Cryogenic Ion Trap. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17 (22), 3723-3739 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201600753.
- Tsybizova, A.; Roithová, J. Copper-catalyzed reactions: Research in the gas phase: COPPER CATALYSIS. Mass Spectrometry Reviews 2016, 35 (1), 85-110 DOI: 10.1002/mas.21464.
- Botha, F.; Slavíčková, M.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Copper-mediated arylsulfanylations and arylselanylations of pyrimidine or 7-deazapurine nucleosides and nucleotides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14 (42), 10018-10022 DOI: 10.1039/C6OB01917J.
- Sabat, N.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. C–H Phosphonation of Pyrrolopyrimidines: Synthesis of Substituted 7- and 9-Deazapurine-8-phosphonate Derivatives. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 81 (19), 9507-9514 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01970.
- Baumgartner, B.; Bojdys, M. J.; Skrinjar, P.; Unterlass, M. M. Design Strategies in Hydrothermal Polymerization of Polyimides. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 2016, 217 (3), 485-500 DOI: 10.1002/macp.201500287.
- Machara, A.; Endoma-Arias, M. Ann A.; Císařová, I.; D. Cox, P.; Hudlicky, T. Direct Synthesis of Noroxymorphone from Thebaine: Unusual Ce IV Oxidation of a Methoxydiene-Iron Complex to an Enone-γ-Nitrate. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 2016 (8), 1500-1503 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201600153.
- Koukal, P.; Ulč, J.; Nečas, D.; Kotora, M. Enantioselective Allylation of β-Haloacrylaldehydes: Formal Total Syntheses of Pteroenone and Antillatoxin. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 2016 (12), 2110-2114 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201600286.
- Matoušová, E.; Koukal, P.; Formánek, B.; Kotora, M. Enantioselective Synthesis of the Unsaturated Fragment of Callyspongiolide. Organic Letters 2016, 18 (21), 5656-5659 DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02897.
- Kielkowski, P.; Cahová, H.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Flexible double-headed cytosine-linked 2′-deoxycytidine nucleotides. Synthesis, polymerase incorporation to DNA and interaction with DNA methyltransferases. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 24 (6), 1268-1276 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.01.057.
- Roithová, J.; Gray, A.; Andris, E.; Jašík, J.; Gerlich, D. Helium Tagging Infrared Photodissociation Spectroscopy of Reactive Ions. Accounts of Chemical Research 2016, 49 (2), 223-230 DOI: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00489.
- Raindlová, V.; Janoušková, M.; Slavíčková, M.; Perlíková, P.; Boháčová, S.; Milisavljevič, N.; Šanderová, H.; Benda, M.; Barvík, I.; Krásný, L.; et al. Influence of major-groove chemical modifications of DNA on transcription by bacterial RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Research 2016, 44 (7), 3000-3012 DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw171.
- Řezanka, P.; Řezanková, K.; Sedláčková, H.; Mašek, J.; Rokosová, L.; Bláhová, M.; Řezanka, M.; Jindřich, J.; Sýkora, D.; Král, V. Influence of substituent position and cavity size of the regioisomers of monocarboxymethyl-α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrins on the apparent stability constants of their complexes with both enantiomers of Tröger's base. Journal of Separation Science 2016, 39 (5), 980-985 DOI: 10.1002/jssc.201500845.
- Güixens-Gallardo, P.; Hocek, M.; Perlíková, P. Inhibition of non-templated nucleotide addition by DNA polymerases in primer extension using twisted intercalating nucleic acid modified templates. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2016, 26 (2), 288-291 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.12.034.
- Škríba, A.; Jašík, J.; Andris, E.; Roithová, J. Interaction of Ruthenium(II) with Terminal Alkynes: Benchmarking DFT Methods with Spectroscopic Data. Organometallics 2016, 35 (7), 990-994 DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.6b00021.
- Albiñana, C. Berenguer; Machara, A.; Řezáčová, P.; Pachl, P.; Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M. Kinetic, thermodynamic and structural analysis of tamiphosphor binding to neuraminidase of H1N1 (2009) pandemic influenza. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 121, 100-109 DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.05.016.
- Ye, S.; Kupper, C.; Meyer, S.; Andris, E.; Navrátil, R.; Krahe, O.; Mondal, B.; Atanasov, M.; Bill, E.; Roithová, J.; et al. Magnetic Circular Dichroism Evidence for an Unusual Electronic Structure of a Tetracarbene–Oxoiron(IV) Complex. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2016, 138 (43), 14312-14325 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b07708.
- Machara, A.; Konvalinka, J.; Kotora, M. A MODULAR SYNTHESIS OF N -BENZOTRIAZOLE UREAS USING ALKYLATION OF 5-NITROBENZOTRIAZOLE. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1 (1), 101-107 DOI: 10.1002/slct.201600025.
- Bednářová, E.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Jindřich, J. Optimized methods for preparation of 6 I -(ω-sulfanyl-alkylene-sulfanyl)-β-cyclodextrin derivatives. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 12, 349-352 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.12.38.
- Nakatani, K.; Tor, Y.; Dadová, J.; Cahová, H.; Hocek, M. Polymerase Synthesis of Base-Modified DNA; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; Vol. 31, pp 123-144.
- Makukhin, N.; Tretyachenko, V.; Moskovitz, J.; Míšek, J. A Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Imaging of the Activity of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A in Cells. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2016, 55 (41), 12727-12730 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201605833.
- Albiñana, C. Berenguer; Hayward, J. J.; Hudlicky, T.; Machara, A. Reinvestigation of acetylation of 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and reconciliation of previously reported analytical data. Tetrahedron Letters 2016, 57 (9), 1019-1021 DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.01.075.
- Dziuba, D.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Cebecauer, M.; Hof, M.; Hocek, M. A Rotational BODIPY Nucleotide: An Environment-Sensitive Fluorescence-Lifetime Probe for DNA Interactions and Applications in Live-Cell Microscopy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2016, 55 (1), 174-178 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201507922.
- Bednářová, E.; Colacino, E.; Lamaty, F.; Kotora, M. A Ruthenium Complex-Catalyzed Cyclotrimerization of Halodiynes with Nitriles. Synthesis of 2- and 3-Halopyridines. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2016, 358 (12), 1916-1923 DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201600127.
- Dziuba, D.; Pospíšil, P.; Matyašovský, J.; Brynda, J.; Nachtigallová, D.; Rulíšek, L.; Pohl, R.; Hof, M.; Hocek, M. Solvatochromic fluorene-linked nucleoside and DNA as color-changing fluorescent probes for sensing interactions. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7 (9), 5775-5785 DOI: 10.1039/C6SC02548J.
- Machara, A.; Lux, V.; Kožíšek, M.; Šašková, K. Grantz; Štěpánek, O.; Kotora, M.; Parkan, K.; Pávová, M.; Glass, B.; Sehr, P.; et al. Specific Inhibitors of HIV Capsid Assembly Binding to the C-Terminal Domain of the Capsid Protein: Evaluation of 2-Arylquinazolines as Potential Antiviral Compounds. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 59 (2), 545-558 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01089.
- Andris, E.; Jašík, J.; Gómez, L.; Costas, M.; Roithová, J. Spectroscopic Characterization and Reactivity of Triplet and Quintet Iron(IV) Oxo Complexes in the Gas Phase. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2016, 55 (11), 3637-3641 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201511374.
- Humpl, M.; Tauchman, J.; Topolovčan, N.; Kretschmer, J.; Hessler, F.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M.; Vesely, J. Stereoselective Synthesis of Ezetimibe via Cross-Metathesis of Homoallylalcohols and α-Methylidene-β-Lactams. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 81 (17), 7692-7699 DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01406.
- Mikušek, J.; Matouš, P.; Matoušová, E.; Janoušek, M.; Kuneš, J.; Pour, M. Substrate Control in the Gold(I)-Catalyzed Cyclization of β - Propargylamino Acrylic Esters and Further Transformations of the Resultant Dihydropyridines. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2016, 358 (18), 2912-2922 DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201600412.
- Benkovics, G.; Hodek, O.; Havlikova, M.; Bosakova, Z.; Coufal, P.; Malanga, M.; Fenyvesi, E.; Darcsi, A.; Beni, S.; Jindřich, J. Supramolecular structures based on regioisomers of cinnamyl-α-cyclodextrins – new media for capillary separation techniques. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 12, 97-109 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.12.11.
- Sabat, N.; Nauš, P.; Matyašovský, J.; Dziuba, D.; Slavětínská, L.; Hocek, M. Synthesis of Fluorescent 2-Substituted 6-(Het)aryl-7-deazapurine Bases {4-(Het)aryl-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines} by Aqueous Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions. Synthesis 2016, 48 (07), 1029-1045 DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1561287.
- Machara, A.; Endoma-Arias, M.; Císařová, I.; Cox, D.; Hudlicky, T. Synthesis of Nororipavine and Noroxymorphone via N- and O-Demethylation of Iron Tricarbonyl Complex of Thebaine. Synthesis 2016, 48 (12), e1-e1 DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1562345.
- Korotvička, A.; Frejka, D.; Hampejsová, Z.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M. Synthesis of Phenanthridines via a Rhodium-Catalyzed C–C Bond Cleavage Reaction of Biphenylene with Nitriles. Synthesis 2016, 48 (07), 987-996 DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1561343.
- Kolská, K.; Ghavre, M.; Pour, M.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Kotora, M. Total Synthesis of Coibacin D by Using Enantioselective Allylation and Metathesis Reactions. Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry 2016, 5 (5), 646-651 DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201600022.
- Havlikova, M.; Bosakova, Z.; Benkovics, G.; Jindřich, J.; Popr, M.; Coufal, P. Use of 6-O-mono-substituted derivatives of β-cyclodextrin-bearing substituent with two permanent positive charges in capillary electrophoresis. Chemical Papers 2016, 70 (9), 1144–1154 DOI: 10.1515/chempap-2016-0053.
- Danhel, A.; Trosanova, Z.; Balintová, J.; Havran, L.; Hocek, M.; Barek, J.; Fojta, M. Voltammetric analysis of 5-(4-Azidophenyl)-2′-deoxycytidine nucleoside and azidophenyl-labelled single- and double-stranded DNAs. Electrochimica Acta 2016, 215, 72-83 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.08.096.
- Kaiser, R. P.; Hessler, F.; Mosinger, J.; Císařová, I.; Kotora, M. A [2+2+2]-Cyclotrimerization Approach to Selectively Substituted Fluorenes and Fluorenols, and Their Conversion to 9,9′-Spirobifluorenes. Chemistry - A European Journal 2015, 21 (39), 13577-13582 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201502370.
- Malnuit, V.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Nauš, P.; Džubák, P.; Hajdúch, M.; Stolaříková, J.; Snášel, J.; Pichová, I.; Hocek, M. 2-Substituted 6-(Het)aryl-7-deazapurine Ribonucleosides: Synthesis, Inhibition of Adenosine Kinases, and Antimycobacterial Activity. ChemMedChem 2015, 10 (6), 1079-1093 DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201500081.
- Kamlar, M.; Císařová, I.; Veselý, J. Alkynylation of heterocyclic compounds using hypervalent iodine reagent. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13 (10), 2884-2889 DOI: 10.1039/C4OB02625J.
- Balintová, J.; Špaček, J.; Pohl, R.; Brázdová, M.; Havran, L.; Fojta, M.; Hocek, M. Azidophenyl as a click-transformable redox label of DNA suitable for electrochemical detection of DNA–protein interactions. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6 (1), 575-587 DOI: 10.1039/C4SC01906G.
- Dadová, J.; Vrábel, M.; Adámik, M.; Brázdová, M.; Pohl, R.; Fojta, M.; Hocek, M. Azidopropylvinylsulfonamide as a New Bifunctional Click Reagent for Bioorthogonal Conjugations: Application for DNA-Protein Cross-Linking. Chemistry - A European Journal 2015, 21 (45), 16091-16102 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201502209.
- Gergelitsová, I.; Tauchman, J.; Císařová, I.; Veselý, J. Bifunctional (Thio)urea–Phosphine Organocatalysts Derived from d-Glucose and α-Amino Acids and Their Application to the Enantioselective Morita–Baylis–Hillman Reaction. Synlett 2015, 26 (19), 2690-2696 DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1560931.
- Gray, A.; Tsybizova, A.; Roithova, J. Carboxylate-assisted C–H activation of phenylpyridines with copper, palladium and ruthenium: a mass spectrometry and DFT study. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6 (10), 5544-5553 DOI: 10.1039/C5SC01729G.
- Olszewska, A.; Dadová, J.; Mačková, M.; Hocek, M. Cleavage of DNA containing 5-fluorocytosine or 5-fluorouracil by type II restriction endonucleases. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 23 (21), 6885-6890 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.09.051.
- Šnajdr, I.; Parkan, K.; Hessler, F.; Kotora, M. Cross-metathesis reaction of α- and β-vinyl C -glycosides with alkenes. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015, 11, 1392-1397 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.11.150.
- Jelinek, I.; Jindřich, J.; Dian, J. The Development of Optical Sensor with Chemically Modified Electroluminescence Diodes. Chemicke Listy 2015, 109 (5), 377-384.
- Banwell, M. G.; Buckler, J. N.; Jackson, C. J.; Lan, P.; Ma, X.; Matoušová, E.; Nugent, J. Devising New Syntheses of the Alkaloid Galanthamine, a Potent and Clinically Deployed Inhibitor of Acetylcholine Esterase; Elsevier, 2015; Vol. 11, pp 29-50.
- A. Downey, M.; Richter, C.; Pohl, R.; Mahrwald, R.; Hocek, M. Direct One-Pot Synthesis of Nucleosides from Unprotected or 5-O-Monoprotected D-Ribose. Organic Letters 2015, 17 (18), 4604-4607 DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02332.
- Koukal, P.; Kotora, M. Enantioselective Allylation of (2E,4E)-2,4-Dimethylhexadienal: Synthesis of (5R,6S)-(+)-Pteroenone. Chemistry - A European Journal 2015, 21 (20), 7408-7412 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201500050.
- Ménová, P.; Dziuba, D.; Güixens-Gallardo, P.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Hof, M.; Hocek, M. Fluorescence Quenching in Oligonucleotides Containing 7-Substituted 7-Deazaguanine Bases Prepared by the Nicking Enzyme Amplification Reaction. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2015, 26 (2), 361-366 DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00006.
- Jašík, J.; Navrátil, R.; Němec, I.; Roithová, J. Infrared and Visible Photodissociation Spectra of Rhodamine Ions at 3 K in the Gas Phase. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2015, 119 (51), 12648-12655 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.5b08462.
- Jašík, J.; Roithová, J. Infrared spectroscopy of CHCl2+ molecular dications. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2015, 377, 109-115 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijms.2014.07.001.
- Schulz, J.; Shcherbachenko, E.; Roithová, J. Investigation of Geminally Diaurated Arene Complexes in the Gas Phase. Organometallics 2015, 34 (16), 3979-3987 DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.5b00343.
- Sabat, N.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Hocek, M. Ir-catalyzed C–H silylations of phenyldeazapurines. Tetrahedron Letters 2015, 56 (49), 6860-6862 DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.10.089.
- Klečka, M.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Hocek, M. Modification of Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines by C-H Borylation Followed by Cross-Coupling or Other Transformations: Synthesis of 6,8-Disubstituted 7-Deazapurine Bases. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015, 2015 (36), 7943-7961 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201501177.
- Mačková, M.; Boháčová, S.; Perlíková, P.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Hocek, M. Polymerase Synthesis and Restriction Enzyme Cleavage of DNA Containing 7-Substituted 7-Deazaguanine Nucleobases. ChemBioChem 2015, 16 (15), 2225-2236 DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201500315.
- Dziuba, D.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Polymerase synthesis of DNA labelled with benzylidene cyanoacetamide-based fluorescent molecular rotors: fluorescent light-up probes for DNA-binding proteins. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51 (23), 4880-4882 DOI: 10.1039/C5CC00530B.
- Popr, M.; Filippov, S. K.; Matushkin, N.; Dian, J.; Jindřich, J. Properties of cationic monosubstituted tetraalkylammonium cyclodextrin derivatives – their stability, complexation ability in solution or when deposited on solid anionic surface. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015, 11, 192-199 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.11.20.
- Jašíková, L.; Anania, M.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Roithová, J. Reaction Intermediates Kinetics in Solution Investigated by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry: Diaurated Complexes. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2015, 137 (42), 13647-13657 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b08744.
- Topolovčan, N.; Panov, I.; Kotora, M. Reaction of Bicyclic Zirconacyclopentenes with Aldehydes and a Potential Pathway to Condensed 5-7-6(Ar) Ring Systems: Reaction of Bicyclic Zirconacyclopentenes with Aldehydes. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015, 2015 (13), 2868-2878 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201500248.
- Nauš, P.; Caletková, O.; Perlíková, P.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Tloušťová, E.; Hodek, J.; Weber, J.; Džubák, P.; Hajdúch, M.; Hocek, M. Synthesis and biological profiling of 6- or 7-(het)aryl-7-deazapurine 4′-C-methylribonucleosides. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 23 (23), 7422-7438 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.10.040.
- Klečka, M.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Tloušťová, E.; Džubák, P.; Hajdúch, M.; Hocek, M. Synthesis and cytostatic activity of 7-arylsulfanyl-7-deazapurine bases and ribonucleosides. Med. Chem. Commun. 2015, 6 (4), 576-580 DOI: 10.1039/C4MD00492B.
- Tokarenko, A.; Slavětínská, L. Poštová; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. Synthesis of Benzene and Pyridine 2-C-Methyl-C-ribonucleosides and -nucleotides. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015, 2015 (36), 7962-7983 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201501219.
- Bednaříková, T.; Tošner, Z.; Horský, J.; Jindřich, J. Synthesis of C 3 -symmetric tri(alkylamino) guests and their interaction with cyclodextrins. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry 2015, 81 (1-2), 141-152 DOI: 10.1007/s10847-014-0443-1.
- Jašík, J.; Gerlich, D.; Roithová, J. Two-Color Infrared Predissociation Spectroscopy of C 6 H 6 2+ Isomers Using Helium Tagging. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2015, 119 (11), 2532-2542 DOI: 10.1021/jp5088064.
- Kielkowski, P.; Fanfrlík, J.; Hocek, M. 7-Aryl-7-deazaadenine 2′-Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphates (dNTPs): Better Substrates for DNA Polymerases than dATP in Competitive Incorporations. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53 (29), 7552-7555 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201404742.
- Šnajdr, I.; Janoušek, Z.; Takagaki, M.; Císařová, I.; Hosmane, N. S.; Kotora, M. Alpha (α-) and beta (β-carboranyl-C-deoxyribosides: Syntheses, structures and biological evaluation. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 83, 389-397 DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.06.005.
- Dziuba, D.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Bodipy-Labeled Nucleoside Triphosphates for Polymerase Synthesis of Fluorescent DNA. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2014, 25 (11), 1984-1995 DOI: 10.1021/bc5003554.
- Cooper, A. I.; Bojdys, M. J. Carbon nitride vs. graphene – now in 2D!. Materials Today 2014, 17 (10), 468-469 DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.001.
- Hocek, M.; Ćerňová, M.; Pohl, R.; Klepetářová, B. C-H Trifluoromethylations of 1,3-Dimethyluracil and Reactivity of the Products in C-H Arylations. HETEROCYCLES 2014, 89 (5), 1159 DOI: 10.3987/COM-14-12958.
- Krömer, M.; Klečka, M.; Slavětínská, L.; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. Chemoselective Synthesis of 4,5-Diarylpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines (6,7-Diaryl-7-deazapurines) by Consecutive Suzuki and Liebeskind-Srogl Cross-Couplings. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 2014 (32), 7203-7210 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201402882.
- Popr, M.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Jindřich, J. A complete series of 6-deoxy-monosubstituted tetraalkylammonium derivatives of α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrin with 1, 2, and 3 permanent positive charges. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 10, 1390-1396 DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.10.142.
- Murphy, B.; Šnajdr, I.; Machara, A.; Endoma-Arias, M. Ann A.; Stamatatos, T. C.; D. Cox, P.; Hudlicky, T. Conversion of Thebaine to Oripavine and Other Useful Intermediates for the Semisynthesis of Opiate-Derived Agents: Synthesis of Hydromorphone. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2014, 356 (11-12), 2679-2687 DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201400445.
- Parkan, K.; Pohl, R.; Kotora, M. Cross-Coupling Reaction of Saccharide-Based Alkenyl Boronic Acids with Aryl Halides: The Synthesis of Bergenin. Chemistry - A European Journal 2014, 20 (15), 4414-4419 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201304304.
- Hessler, F.; Kulhavá, L.; Císarˇová, I.; Otmar, M.; Kotora, M. Cycloaddition Reactions of Deoxyribosylpropynoates. Synthetic Communications 2014, 44 (9), 1232-1239 DOI: 10.1080/00397911.2013.848896.
- Sabat, N.; Klečka, M.; Slavětínská, L.; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. Direct C-H amination and C-H chloroamination of 7-deazapurines. RSC Adv. 2014 DOI: 10.1039/C4RA13143F.
- Danhel, A.; Raindlová, V.; Havran, L.; Pivonkova, H.; Hocek, M.; Fojta, M. Electrochemical behaviour of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazi(o)ne as multi-redox centre DNA label at mercury meniscus modified silver solid amalgam electrode. Electrochimica Acta 2014, 126, 122-131 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.09.147.
- Hessler, F.; Betík, R.; Kadlcikova, A.; Belle, R.; Kotora, M. Enantioselective Allylation of Selected ortho-Substituted Benzaldehydes: A Comparative Study. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 2014 (32), 7245-7252 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201403034.
- Cadart, T.; Koukal, P.; Kotora, M. Enantioselective Allylation of tert-Butyldimethylsilyl-Protected Vanillin and Synthesis of a Lignan Derivative Isolated from Machilus wangchiana. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 2014 (34), 7556-7560 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201403094.
- Motloch, P.; Valterová, I.; Kotora, M. Enantioselective Allylation of Thiophene-2-carbaldehyde: Formal Total Synthesis of Duloxetine. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2014, 356 (1), 199-204 DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201300849.
- Vesely, J.; Rios, R. Enantioselective methodologies using N-carbamoyl-imines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43 (2), 611-630 DOI: 10.1039/C3CS60321K.
- Hanzlová, E.; Váňa, J.; Shaffer, C. J.; Roithová, J.; Martinů, T. Evidence for the Cyclic CN 2 Carbene in the Gas Phase. Organic Letters 2014, 16 (20), 5482-5485 DOI: 10.1021/ol5027602.
- Kurka, O.; Roithová, J.; Bednář, P. Examination of small molecule losses in 5-methylpyranopelargonidin MS/MS CID spectra by DFT calculations: MS/MS and DFT of 5-methylpyranopelargonidin. Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2014, 49 (12), 1314-1321 DOI: 10.1002/jms.3466.
- Jakl, M.; Straka, M.; Dytrtová, J. Jaklová; Roithová, J. Formation and stability of calcium complexes of dimethyl sulfoxide in water. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2014, 360, 8-14 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijms.2014.01.001.
- Tsybizova, A.; Schröder, D.; Roithová, J.; Henke, A.; Šrogl, J. Gas-phase studies of copper catalyzed aerobic cross coupling of thiol esters and arylboronic acids: REACTION MECHANISMS. Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry 2014, 27 (3), 198-203 DOI: 10.1002/poc.3262.
- Baumgartner, B.; Bojdys, M. J.; Unterlass, M. M. Geomimetics for green polymer synthesis: highly ordered polyimides via hydrothermal techniques. Polymer Chemistry 2014, 5 (12), 3771 DOI: 10.1039/c4py00263f.
- Řezanka, P.; Rokosová, L.; Řezanková, K.; Bláhová, M.; Řezanka, M.; Sýkora, D.; Jindřich, J.; Král, V. The influence of the substituent position in monocarboxymethyl-γ-cyclodextrins on enantioselectivity in capillary electrophoresis. Journal of Separation Science 2014, 37 (19), 2779-2784 DOI: 10.1002/jssc.201400604.
- Hývl, J.; Roithová, J. Mass Spectrometric Studies of Reductive Elimination from Pd(IV) Complexes. Organic Letters 2014, 16 (1), 200-203 DOI: 10.1021/ol403190g.
- Prchalová, E.; Štěpánek, O.; Smrček, S.; Kotora, M. Medicinal applications of perfluoroalkylated chain-containing compounds. Future Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 6 (10), 1201-1229 DOI: 10.4155/fmc.14.53.
- Simonova, A.; Balintová, J.; Pohl, R.; Havran, L.; Fojta, M.; Hocek, M. Methoxyphenol and Dihydrobenzofuran as Oxidizable Labels for Electrochemical Detection of DNA. ChemPlusChem 2014, n/a-n/a DOI: 10.1002/cplu.201402194.
- Tumova, L.; Pombinho, A. R.; Vojtechova, M.; Stancikova, J.; Gradl, D.; Krausova, M.; Sloncova, E.; Horazna, M.; Kriz, V.; Machonova, O.; et al. Monensin inhibits canonical wnt signaling in human colorectal cancer cells and suppresses tumor growth in multiple intestinal neoplasia mice. Molecular cancer therapeutics 2014, 13 (4), 812-822 DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0625.
- Škríba, A.; Schulz, J.; Roithová, J. Monitoring of Reaction Intermediates in the Gas Phase: Ruthenium-Catalyzed C–C Coupling. Organometallics 2014, 33 (23), 6868-6878 DOI: 10.1021/om500933w.
- Putaj, P.; Tichá, I.; Císařová, I.; Vesely, J. One-Pot Preparation of Chiral Carbacycles from Morita-Baylis-Hillman Carbonates by an Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation/Olefin Metathesis Sequence: One-Pot Preparation of Chiral Carbacycles. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 2014 (30), 6615-6620 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201402899.
- Kamlar, M.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Císařová, I.; Veselý, J. Organocatalytic enantioselective allylic alkylation of MBH carbonates with β-keto esters. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2014, 12 (28), 5071 DOI: 10.1039/c4ob00682h.
- Tsybizova, A.; Remeš, M.; Vesely, J.; Hybelbauerová, S.; Roithová, J. Organocatalytic Preparation of Substituted Cyclopentanes: A Mechanistic Study. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 79 (4), 1563-1570 DOI: 10.1021/jo4022106.
- Mačková, M.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Polymerase Synthesis of DNAs Bearing Vinyl Groups in the Major Groove and their Cleavage by Restriction Endonucleases. ChemBioChem 2014, 15 (15), 2306-2312 DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201402319.
- Vaníková, Z.; Hocek, M. Polymerase Synthesis of Photocaged DNA Resistant against Cleavage by Restriction Endonucleases. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53 (26), 6734-6737 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201402370.
- Jašík, J.; Gerlich, D.; Roithová, J. Probing Isomers of the Benzene Dication in a Low-Temperature Trap. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136 (8), 2960-2962 DOI: 10.1021/ja412109h.
- Váňa, J.; Roithová, J.; Kotora, M.; Beran, P.; Rulíšek, L.; Kočovský, P. Proton Affinities of Organocatalysts Derived from Pyridine N-oxide. Croatica Chemica Acta 2014, 87 (4), 349-356 DOI: 10.5562/cca2447.
- Schulz, J.; Jašíková, L.; Škríba, A.; Roithová, J. Role of Gold(I) α-Oxo Carbenes in the Oxidation Reactions of Alkynes Catalyzed by Gold(I) Complexes. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136 (32), 11513-11523 DOI: 10.1021/ja505945d.
- Tsybizova, A.; Ryland, B. L.; Tsierkezos, N.; Stahl, S. S.; Roithová, J.; Schröder, D. Speciation Behavior of Copper(II) Acetate in Simple Organic Solvents - Revealing the Effect of Trace Water: Speciation Behavior of Cu(II) Acetate in Simple Organic Solvents. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry 2014, 2014 (8), 1407-1412 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201400036.
- Snášel, J.; Nauš, P.; Dostál, J.; Hnízda, A.; Fanfrlík, J.; Brynda, J.; Bourderioux, A.; Dušek, M.; Dvořáková, H.; Stolaříková, J.; et al. Structural Basis for Inhibition of Mycobacterial and Human Adenosine Kinase by 7-Substituted 7-(Het)aryl-7-deazaadenine Ribonucleosides. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 57 (20), 8268-8279 DOI: 10.1021/jm500497v.
- Ceban, V.; Putaj, P.; Meazza, M.; Pitak, M. B.; Coles, S. J.; Vesely, J.; Rios, R. Synergistic catalysis: highly diastereoselective benzoxazole addition to Morita–Baylis–Hillman carbonates. Chemical Communications 2014, 50 (56), 7447 DOI: 10.1039/c4cc00728j.
- Hessler, F.; Korotvička, A.; Nečas, D.; Valterová, I.; Kotora, M. Syntheses of a Flobufen Metabolite and Dapoxetine Based on Enantioselective Allylation of Aromatic Aldehydes: Syntheses of a Flobufen Metabolite and Dapoxetine. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 2014 (12), 2543-2548 DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201301899.
- Nauš, P.; Caletková, O.; Konečný, P.; Džubák, P.; Bogdanová, K.; Kolář, M.; Vrbková, J.; Slavětínská, L.; Tloušt’ová, E.; Perlíková, P.; et al. Synthesis, Cytostatic, Antimicrobial, and Anti-HCV Activity of 6-Substituted 7-(Het)aryl-7-deazapurine Ribonucleosides. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 57 (3), 1097-1110 DOI: 10.1021/jm4018948.
- Hocek, M. Synthesis of Base-Modified 2′-Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphates and Their Use in Enzymatic Synthesis of Modified DNA for Applications in Bioanalysis and Chemical Biology. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2014, 79 (21), 9914-9921 DOI: 10.1021/jo5020799.
- Dhami, K.; Malyshev, D. A.; Ordoukhanian, P.; Kubelka, T.; Hocek, M.; Romesberg, F. E. Systematic exploration of a class of hydrophobic unnatural base pairs yields multiple new candidates for the expansion of the genetic alphabet. Nucleic Acids Research 2014, 42 (16), 10235-10244 DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku715.
- Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; et al. Triazine-Based Graphitic Carbon Nitride: a Two-Dimensional Semiconductor. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53 (29), 7450-7455 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201402191.
- Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; et al. Triazine-Based Graphitic Carbon Nitride: a Two-Dimensional Semiconductor. Angewandte Chemie 2014, 126 (29), 7580-7585 DOI: 10.1002/ange.201402191.
- Danhel, A.; Raindlová, V.; Havran, L.; Barek, J.; Hocek, M.; Fojta, M. Voltammetric Study of dsDNA Modified by Multi-redox Label Based on N-methyl-4-hydrazino-7-nitrobenzofurazan. Electrochimica Acta 2014, 129, 348-357 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2014.02.137.






















